For this reason, intraoperative neuromonitoring (IONM) has been established for many years, especially in the field of facial nerve surgery >> to support surgeons in locating the nerve branches and thus increasing patient safety.
Neuromonitoring in facial nerve surgery is used in two ways:
Where tympanoplasty is performed or a cochlear implant inserted, inomed's neuromonitoring is a useful tool that helps prevent nerve injury during milling near the bony facial canal. During mastoidectomy procedures, neuromonitoring techniques are used to reduce the risk of nerve injury.
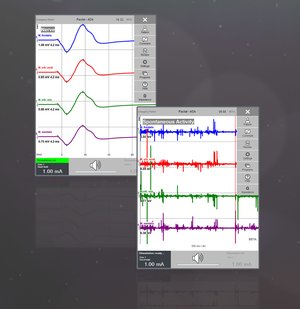
A hand-held stimulation probe locates nerve branches during facial nerve surgery. Every channel and thus every nerve makes a different sound allowing acoustic identification of the nerve by the so-called Channel Ident function.
Bipolar probes are highly selective and can be used to monitor nerve branches and their function in the immediate vicinity, whereas monopolar probes have a wider field of action. Electrodes are placed in the corresponding indicator muscle to record electrophysiological signals. If there is any significant change in the amplitude or latency of the muscle responses during surgery, the surgeon is informed visually and acoustically. This also happens if spontaneous activity should occur. Any spontaneous activity detected is automatically recorded and can be annotated for documentation.
The C2 Xplore >> with its wide field of application, provides innovative solutions for optimum surgical performance by its HL7-Ready interface to the hospital network and its intuitive comment function which monitors relevant events at all times.